Uncategorized
Failing Productively
As an entrepreneur, you will typically get advice like, “Fail fast and fail often.” I always found this somewhat amusing, similar to the saying, “It takes money to make money” (a lot of bad investments are made using that philosophy). Living this yourself is an amazing experience – especially when things turn out well. But as I have written about before, you learn as much from the good experiences as you do from the bad ones.
Innovating is tough. You need people who always think of different and better ways of doing things or question why something has to be done or made a certain way. It means shifting away from the “how” and “why” and focusing on the “what” (outcomes). It takes confidence to ask questions that many would view as stupid (“Why would you do that, it’s always been done this way.”) But, when you have the right mix of people and culture, amazing things can and do happen, and it feels great.
Innovating also takes a willingness to lose time and money, hoping to win something big enough later to make it all worthwhile. This is where many companies fall short because they lack the patience, budget, or appetite to fail. I personally believe that this is the reason why innovation often flows from small companies and small teams. For them, the prospect of doing something cool or making a big impact is motivation enough to try something, and the barriers to getting started are often much lower.
It takes a lot of discipline to follow a plan when a project appears to be failing, but it takes even more discipline to kill a project that has demonstrated real potential but isn’t meeting expectations. That was one of my first and probably most important lessons learned in this area. Let me explain…
In 2000 we looked at franchising our “Consulting System” – processes, procedures, tools, metrics, etc., developed and proven in my business. We believed this approach could help average consultants deliver above-average work products in less time. The idea seemed to have real potential.
Finding an attorney who would even consider this idea took a lot of work. Most believed it would be impossible to proceduralize a somewhat ambiguous task like solving a business or technical problem. We finally found an attorney who, after a 2-hour no-cost interview, agreed to work with us. When asked about his approach, he replied, “I did not want to waste my [his] time or our money on a fool’s errand.”
We estimated it would take 12 months and cost approximately $100,000 to fully develop our consulting system. We met with potential prospects to validate the idea (it would have been illegal to pre-sell the system) and then got to work. Twelve months turned into 18, and the original $100K budget increased nearly 50%. All indications were positive, and we felt very good about the success and business potential of this effort.
Then, the terror attacks occurred on Sept. 11th and businesses everywhere saw a decline. In early 2002 we reevaluated the project and felt that it could be completed within the next 6-8 months and would cost another $50K+.
After a long and emotional debate, we decided to kill the project – not because we felt it would not work, but because there was less of a target market, and now the payback period (time to value) would double or triple. This was one of the most difficult business decisions that I ever made.
A big lesson learned from this experience was that our approach needed to be more analytical.
- From that point forward, we created a budget for “time off” (we bought our own time, as opposed to waiting for bench time) and other project-related items.
- We developed a simple system for collecting and tracking ideas and feedback. When an idea felt right, we would take the next steps and create a plan with a defined budget, milestones, and timeline. If the project failed to meet any defined objectives, it would be killed – No questions asked.
- We documented what we did, why we decided to do it, our goals, and expected outcomes and timelines. Regardless of success or failure, we would conduct postmortem reviews to learn and document as much as possible from every effort and investment.
We still had failures, but with each one, we took less time and spent less money. More importantly, we learned how to do this better, which helped us realize several successes. It provided both the structure and the freedom to create some amazing things. Since failing was an acceptable outcome, it was never feared.
This approach was more than just “failing fast and failing often”; it was “intelligent failure,” which served us well for nearly a decade.
Profitability through Operational Efficiency
In my last post, I discussed the importance of proper pricing for profitability and success. As most people know, you increase profitability by increasing revenue and/or decreasing costs. However, cost reduction does not necessarily mean slashing headcount, wages, benefits, or other factors that often negatively affect morale and cascade negatively on quality and customer satisfaction. There is often a better way.

The best businesses generally focus on repeatability and reliability, realizing that the more you do something – the better you should get at doing it well. You develop a compelling selling story based on past successes, develop a solid reference base, and have identified the sweet spot from a pricing perspective. People keep buying what you are selling, and if your pricing is right, money is available at the end of the month to fund organic growth and operational efficiency efforts.
Finding ways to increase operational efficiency is the ideal way to reduce costs, but it takes time and effort. Sometimes this is realized through increases in experience and skill. But, often optimization occurs through standardization and automation. Developing a system that works well, consistently applying it, measuring and analyzing the results, and then making changes to improve the process. An added benefit is that this approach increases quality, making your offering even more attractive.
Metrics should be collected at a “work package” level or lower (e.g., task level), which means they are related tasks at the lowest level that produce a discrete deliverable. This project management concept works whether you are manufacturing something (although a Bill of Materials may be a better analogy in this segment), building something, or creating something. This allows you to accurately create and validate cost and time estimates. When analyzing work at this level of detail, it becomes easier to identify ways to simplify or automate the process.
When I had my company, we leveraged this approach to win more business with competitive fixed-price project bids that provided healthy profit margins for us while minimizing risk for our clients. Bigger profit margins allowed us to invest in our own growth and success by funding ongoing employee training and education, innovation efforts, and international expansion, as well as experimenting with new things (products, technology, methodology, etc.) that were fun and often taught us something valuable.
Those growth activities were only possible because we focused on doing everything as efficiently and effectively as possible, learning from everything we did – good and bad, and having a tangible way to measure and prove that we were constantly improving.
Think like a CEO, act like a COO, and measure like a CFO. Do this and make a real difference in your own business!
The Importance of Proper Pricing
Pricing is one of those things that can make or break a company. Doing it right takes an understanding of your business (cost structure and growth / profitability goals), the market, your competition, and more. Doing it wrong can mean the death of your business (fast or slow), the inability to attract and retain the best talent, as well as creating a situation where you will no longer have the opportunity to reach your full potential.
These problems apply to companies of all sizes – although large organizations are often better positioned to absorb the impact of bad pricing decisions or sustain an unprofitable business unit. Understanding all possible outcomes is an important aspect of pricing related to risk and risk tolerance.
When I started my consulting company in 1999, we planned to win business by pricing our services 10%-15% lower than the competition. It was a bad plan that didn’t work. Unfortunately, this approach is something you see all too often in businesses today.
We only began to grow after increasing our prices (about 10% more than the competition) and focused on justifying that with our expertise and the value provided. We were (correctly) perceived as a premium alternative, and that positioning helped us grow.
Several years ago, I had a management consulting engagement with a small software company. The business owner told me they were “an overnight success 10 years in the making.” His concern was that they might not be able to capitalize on recent successes, so he was looking for an outside opinion.
I analyzed his business, product, customers, and competition. His largest competitor is the industry leader in this space, and products from both companies were evenly matched from a feature perspective. My client’s product even had a few key features that were better for management and compliance in Healthcare and Union environments that his larger and more popular competitor lacked. So, why weren’t they growing faster?
I found that competition was priced 400% higher for the base product. When I asked the owner, he told me their goal was to be priced 75% – 80% less than the competition. He could not explain why he did this other than to state that he believed that his customers would be unwilling to pay any more than that. His lack of confidence in his product became evident to companies interested in his solution.
He often lost head-to-head competition against that competitor, but almost never on features. Areas of concern were generally the size and profitability of the company and the risk created by each for prospects considering his product.
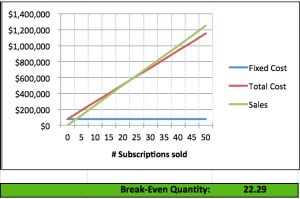
I shared the graph (below) with this person, explaining how proper pricing would increase their profitability and annual revenue and how both of those items would help provide customers and prospects with confidence. Moreover, this would allow the company to grow, eliminate single points of failure in key areas (Engineering and Customer Support), add features, and even spend money on marketing. Success breeds success!
In another example, I worked with the Product Manager of a large software company responsible for producing quarterly product package distributions. This work was outsourced, and each build cost approximately $50K. I asked, “What is the break-even point for each distribution?” That person replied, “There really isn’t a good way to tell.”
By the end of the day, I provided a Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) analysis spreadsheet that showed the break-even point. Even more important, it showed the contribution margin and demonstrated there was very little operating leverage provided these products (i.e., they weren’t very profitable even if you sold many of them).
My recommendations included increasing prices (which could negatively impact sales), investing in fewer releases per year, or finding a more cost-effective way of releasing those products. Without this analysis their “business as usual” approach would have likely continued for several years.
Companies are in business to make money – pure and simple. Everything you do as a business owner or leader needs to be focused on growth. Growth is the result of a combination of factors, such as the uniqueness of the product or services provided, quality, reputation, efficiency, and repeatability. Many of these are the same factors that also drive profitability. Proper pricing can help predictably drive profitability, and having excess profits to invest can significantly impact growth.
Some customers and prospects will do everything possible to whittle your profit margins down to nothing. They are focused on their own short-term gain and not on the long-term risk created for their suppliers. Those same “frugal” companies expect to profit from their own business, so it is unreasonable to expect anything less from their suppliers.
My feeling is that “Not all business is good business,” so it is better to walk away from bad business in order to focus on the business that helps your company grow and be successful.
One of the best books on pricing I’ve ever found is “The Strategy and Tactics of Pricing: A Guide to Profitable Decision Making” by Thomas T. Nagle and Reed K. Holden. I recommend this extremely comprehensive and practical book to anyone responsible for pricing or with P&L responsibility within an organization. It addresses the many complexities of pricing and is truly an invaluable reference.
In a future post, I will write about the metrics I use to understand efficiency and profitability. Metrics can be your best friend when optimizing pricing and maximizing profitability. This can help you create a systematic approach to business that increases efficiency, consistency, and quality.
At my company we developed a system where we know how long common tasks would take to complete, and had efficiency factors for each consultant. This allowed us to create estimates based on the type of work and the people most likely to work on the task and fix-bid the work. Our bids were competitive, and even when we were the highest-priced bid we often won because we would be the only (or one of the few) companies to guarantee prices and results. Our level of effort estimates were +/- 4%, and that helped us maintain a 40%+ minimum gross margin for every project. This analytical approach helped our business double in revenue without doubling in size.
There are many causes of poor pricing, including a lack of understanding of cost structure; Lack of understanding of the value provided by a product or service; Lack of understanding of the level of effort to create, maintain, deliver, and improve a product or service; and Lack of concern for profitability (e.g., salespeople who are paid on the size of the deal, and not on margins or profitability).
But, with a little understanding and effort, you can make small adjustments to your pricing approach and models that can have a huge impact on your business’s bottom line.
Doing it like Mike
My son is playing basketball this year (previously, he played football and soccer), and recently we went shopping for new shoes. Each store had pictures of Michael Jordan. I used to love watching MJ play with the Chicago Bulls. He was the epitome of skill and professionalism. To this day, he inspires me.
Some people are naturally talented but must still work hard to achieve their full potential. Hard work is an important aspect of being the best at anything, but it takes more than that. It takes doing things in a manner that allows you to continuously improve, as well as a positive mindset and a commitment to success. Once people reach that high-performance level, their jobs look easy, and they may even appear to be a “natural” – just like Mike. But that is just the tip of the iceberg.
Most of my career changes have been unplanned. Opportunities presented themselves, the job seemed interesting, and before I knew it, I was fully immersed in something related but different. The potential reward outweighed the real risk.
Many of these things have not come naturally to me. Each time I focused on understanding the requirements for doing the job well, then looked for examples of exceptional performance, and finally created a systematic approach that allowed me to measure performance and identify areas of improvement on an ongoing basis. From then on it was analyzing my results, thinking daily about even the smallest improvements, and then trying to do even better the next day.
Good enough was never good enough. Introspection can be challenging, so one thing that I have done is to take time to celebrate wins and intentionally focus on remembering how that feels. Those memories can be motivational in times of stress or frustration and help you get back on track quickly.
Sales have been a large part of my consulting management jobs since the mid-1990s, but it wasn’t until I owned my own company that this became a true priority. I ran across a good book, The Accidental Salesperson, by Chris Lytle. Back then, Chris Lytle had “MAX Training,” and a large part of their focus was increasing your “level” with regard to Prospect and Client relationships. The training was good and was complementary to systems like Miller Heiman.
What each of these systems do is help you prepare, plan, and execute to the best of your ability. And just like basketball, it takes practice to master. With mastery comes success and the illusion that something is easy (or you are lucky). The Seneca quote, “Luck is what happens when preparation meets opportunity,” is so true.
Regardless of the system used, what is most important is that you are trying to be the best at is to look at both positive and negative examples to see what you can learn from them. There are lessons to be learned everywhere! Understanding what makes it good or bad helps you improve as part of an ongoing improvement process.
Incorporating new tools and techniques into what has already been proven to work will help you improve your game. Returning to the sports analogy, this could be part of what made Michael Jordon so good. He would see something interesting, improve it, and then make it his own.
For example, I get many horrible sales calls and emails. The people have obviously not done any preparation, do not know anything about me or the company I work for, and often remind me of why I stopped listening to them by referring to the number of times they have tried contacting me. On the other hand, some talented sales professionals have done their homework, understand their products and the competition, and understand why what they are selling should matter to me – and can articulate that quickly and confidently. I will speak with them and occasionally buy from them. And in either case I provide my team with real-life examples of good and bad sales techniques.
So, think of the best example of whatever it is you do, and see what you can do to become more like them. This isn’t about imitation but rather about uncovering the secrets of their success and learning from them. And have some fun doing it!
A missed opportunity for Geospatial
I have a Corvette that I like to work on for fun and relaxation. It gives me an excuse to learn something new and an opportunity to hone my troubleshooting skills. It can be a fun way to spend a few hours on a weekend.
A few weekends ago I was looking for a few parts for a small project. This was spur of the moment and really didn’t need to be done now (as the car will be stored soon for the winter). I found the parts I needed from a single company, but then something strange happened.
This website had my address, knew the two parts that I wanted, but failed to make the process easy and almost lost a sale. I needed to manually check five different store locations to see if they had both parts. In this case two of the five did. One store was about 5 miles from my house and the other about 20 miles away.
Just think how helpful it would have been for this website to use the data available (i.e., inventory and locations) and present me with the two options or better yet default me to the closest store and note the other store as an option. Using spatial features this would be extremely easy to implement. It’s the equivalent to the “Easy Button” that one office supply uses in their commercials.
Now, take this example one step further. The website makes things quick and easy, leaving me with a very pleasant shopping experience. It could then recommend related items (it did, but by that time I had wasted more time than necessary and was questioning whether or not I should start that project that day). The website could have also created a simple package offer to try to increase my shopping cart value.
All simple things that would generate more money through increased sales and larger sales. It would seem that this would be very easy to justify from both a business and technical perspective, assuming the company is even aware of this issue.
I frequently tell my team that, “People buy easy.” Help them understand what they need to accomplish their goals, price it fairly, demonstrate the value, and they make the rest of the sales process easy to complete. This makes happy customers and leads to referrals. It just makes good business sense to do this.
So, while geospatial technology might not be the solution to all problems, this is a specific use case where it would. The power of computing systems and applications today is that there is so much that can be done so fast, often for reasonably low investment costs in technology. But the first step getting there is to ask yourself, “How could we be making this process easier for our customers?”
A little extra effort and insight can have a huge payoff.