Latest Event Updates
The Value Created by a Strong Team
I participated in an amazing team-building exercise as a Board Member for the Children’s Hospital Foundation of Wisconsin. We were going down a path that led to a decision on whether or not to invest $150M in a new addition. The CEO at the time, Jon Vice, wisely determined that strong teams were needed for each committee in order to thoroughly vet the idea from every possible perspective.

The process started with being given a book to read (“Now, Discover Your Strengths” by Marcus Buckingham & Donald O. Clifton, Ph.D.) and then completing the “Strengthsfinder” assessment using a code provided in the book. The goal was to understand gaps in perception (how you view yourself vs. how others view you) so that you could truly understand your own strengths and weaknesses. Then, teams were created with people having complementary skills to help eliminate weaknesses from the overall team perspective. The results were impressive.
Over my career, I have been involved in many team-building exercises and events – some of which provided useful insights. However, most failed to combine the findings meaningfully, provide useful context, or offer actionable recommendations. Key areas that were consistently omitted were Organizational Culture, Organizational Politics, and Leadership. Those three areas significantly impact value creation vis-à-vis team effectiveness and commitment.
When I had my consulting company, we had a small core team of business and technology consultants and would leverage subcontractors and an outsourcing company to allow us to take on more concurrent projects as well as larger, more complex projects. This approach worked for three reasons:
- We had developed a High-Performance Culture that was based on:
- Purpose: A common vision of success, understanding why that mattered, and understanding how that was defined and measured.
- Ownership: Taking responsibility for something and being accountable for the outcome. This included responsibility for the extended team of contractors. Standardized procedures helped ensure consistency and make it easier for each person to accept responsibility for “their team.”
- Trust: Everyone understood that they not only needed to trust and support each other, but in order to be effective and responsive, the others would need to trust their judgment. If there was a concern, we would focus on the context and process improvements to understand what happened and implement changes based on lessons learned. Personal attacks were avoided for the good of the entire team.
- Empowerment: Everyone understood that there was risk associated with decision-making while at the same time realizing that delaying an important decision could be costly and create more risk. Therefore, it was incumbent upon each member to make good decisions as needed and then communicate changes to the rest of the team.
- Clear and Open Communication: The people on the team were very transparent and honest. When there was an issue, they would attempt to resolve it first with that person and then escalate if they could not reach an agreement and decided to seek the team’s consensus. Everything was out in the open and done in the spirit of being constructive and collaborating. Divisiveness is the antithesis of this tenet.
People who were not a good fit would quickly wash out, so our core team consisted of trusted experts. A friendly competition helped raise the bar for the entire team, but when needed, the other team members became a safety net for each other.
We were all focused on the same goal, and everyone realized that the only way to be successful was to work together for the team’s success. Win or lose, we did it together. The strength of our team created tremendous value – internally and for our customers that we sustained for several years. That value included innovation, higher levels of productivity and profitability, and an extremely high success rate.
This approach can work at any level but is most effective when it starts at the top. When employees see their company leaders behaving in this manner, it provides the model and sets expectations for everyone under them. If there is dysfunction within an organization, it often starts at the top – by promoting or accepting behaviors that do not benefit the whole of the organization. But, with a strong and positive organizational culture, the value of strong teams is multiplied and becomes an incredible competitive advantage.
Good Article on Why AI Projects Fail

Today I ran across this very good article as it focused on lessons learned, which potentially helps everyone interested in these topics. It contained a good mix of problems at a non-technical level.
Below is the link to the article and commentary on the Top 3 items listed from my perspective.
https://www.cio.com/article/3429177/6-reasons-why-ai-projects-fail.html
Item #1:
The article discusses how the “problem” being evaluated was misstated using technical terms. At least some of these efforts are conducted “in a vacuum.” Given the cost and strategic importance of getting these early-adopter AI projects right, that was a surprise.
In Sales and Marketing, you start the question, “What problem are we trying to solve?” and evolve that to, “How would customers or prospects describe this problem in their own words?” Without that understanding, you can neither initially vet the solution nor quickly qualify the need for your solution when speaking with those customers or prospects. That leaves room for error when transitioning from strategy to execution.
Increased collaboration with Business would likely have helped. This was touched on at the end of the article under “Cultural challenges,” but the importance seemed to be downplayed. Lessons learned are valuable – especially when you are able to learn from the mistakes of others. This should have been called out early as a major lesson learned.
Item #2:
This second area had to do with the perspective of the data, whether that was the angle of the subject in photographs (overhead from a drone vs horizontal from the shoreline) or the type of customer data evaluated (such as from a single source) used to train the ML algorithm.
That was interesting because assumptions may have played a part in overlooking other aspects of the problem, or the teams may have been overly confident about obtaining the correct results using the data available. In the examples cited, those teams figured out those problems and took corrective action. A follow-up article describing the process used to determine the root cause in each case would be very interesting.
As an aside, from my perspective, this is why Explainable AI is so important. Sometimes, you just don’t know what you don’t know (the unknown unknowns). Understanding why and on what the AI is basing its decisions should help with providing better quality curated data up-front, as well as identifying potential drifts in the wrong direction while it is still early enough to make corrections without impacting deadlines or deliverables.
Item #3:
This didn’t surprise me but should be a cause for concern as advances are made at faster rates, and potentially less validation is made as organizations race to be first to market with some AI-based competitive advantage. The last paragraph under ‘Training data bias’ stated that based on a PWC survey, “only 25 percent of respondents said they would prioritize the ethical implications of an AI solution before implementing it.”
Bonus Item:
The discussion about the value of unstructured data was very interesting, especially when you consider:
- The potential for NLU (natural language understanding) products in conjunction with ML and AI.
- This is a great NLU-pipeline diagram from North Side Inc. in Canada, one of the pioneers in this space.
- The importance of semantic data analysis relative to any ML effort.
- The incredible value that products like MarkLogic’s database or Franz’s AllegroGraph provide over standard Analytics Database products.
- I personally believe that the biggest exception to this assertion will be from GPU databases (like OmniSci) that easily handle streaming data, can accomplish extreme computational feats well beyond those of traditional CPU-based products, and have geospatial capabilities that provide an additional dimension of insight to the problem being solved.
Update: This is a link to a related article that discusses trends in areas of implementation, important considerations, and the potential ROI of AI projects: https://www.fastcompany.com/90387050/reduce-the-hype-and-find-a-plan-how-to-adopt-an-ai-strategy
This is definitely an exciting space that will experience significant growth over the next 3-5 years. The more information, experiences, and lessons learned are shared, the better it will be for everyone.
Apollo 11 50th Anniversary – Interesting photos & article link
I still remember my parents letting me stay up late to watch the first moonwalk. It was 9:30 pm, I was 5 years old, and we were huddled around an old “black and white” television with a circular viewing area. My parents tried to convey how important and monumental that moment was – telling me I would tell my children this story someday.
What I remember most was being amazed at seeing the astronauts hop around easily  and not understating how that could be. We had watched the launch on TV and were getting updates nightly from Walter Cronkite on the evening news. Normally my dad would sit at a TV table to eat dinner and watch the news as my mom sat with my sister and me at our kitchen table, but this week was different.
and not understating how that could be. We had watched the launch on TV and were getting updates nightly from Walter Cronkite on the evening news. Normally my dad would sit at a TV table to eat dinner and watch the news as my mom sat with my sister and me at our kitchen table, but this week was different.
With all of the news this past week on the 50th 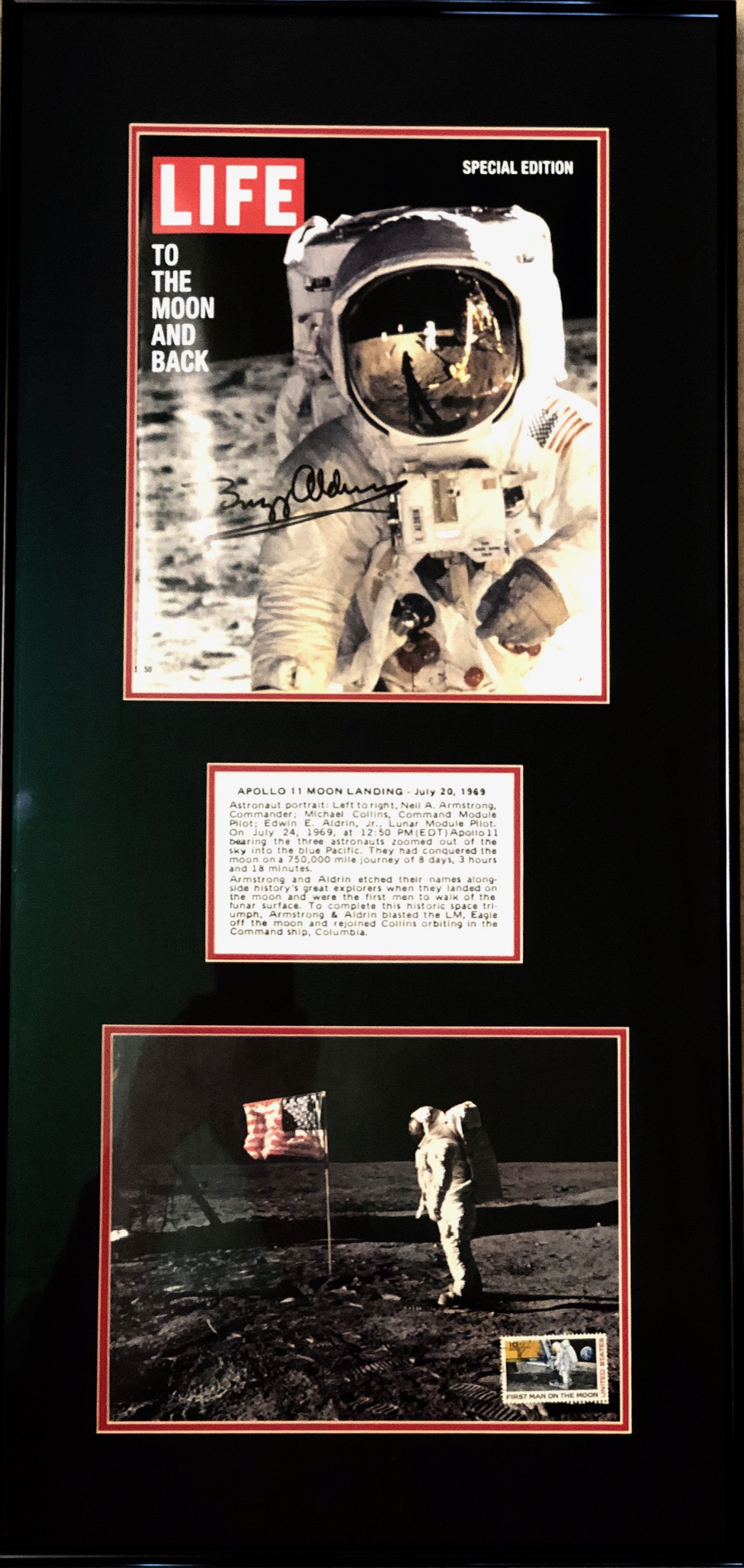 Anniversary of the first moonwalk, it triggered a couple of memories. One of them was that I purchased a collectible item in 2005 at the annual Children’s Circle of Care leadership conference in San Diego, CA. A luncheon was held on the USS Midway Museum deck, and afterward, I took a tour. It is an incredible place to visit if you are ever near San Diego.
Anniversary of the first moonwalk, it triggered a couple of memories. One of them was that I purchased a collectible item in 2005 at the annual Children’s Circle of Care leadership conference in San Diego, CA. A luncheon was held on the USS Midway Museum deck, and afterward, I took a tour. It is an incredible place to visit if you are ever near San Diego.
Before leaving that day, I went to the gift shop to get my wife and children a few trinkets. What I found was a beautiful display, which I immediately purchased and shipped home. This display was taken to school a couple of times for “show and tell.” It hung on my office wall for 3 years and then went into storage with other artwork. It then sat for the past decade, and I almost forgot it.
To me, this display is both beautiful to see and very inspirational as well. Human creativity is an incredible thing! As an aside, I have never seen anything like this display, so I thought I would share it with you.
Today I also ran across a good article regarding this event that provided information I had not seen before. It is very interesting and can be found here: https://go.usa.gov/xyVGh
Edit: This was another good article that discusses the advanced flight control computer used at the time – https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/apollo-11-moon-landings-fourth-crew-member-computer-far-fishman/
This anniversary is a great reminder of the power of individuals, teams, and partnerships when they are mission-focused. I find people like the men and women of NASA to be extremely motivational, and the few I have met have all been very friendly people. They are the humble heroes!

Commentary on an HBR article about Start-ups & Entrepreneurship
A friend posted this article on LinkedIn.com. Due to character limitations for comments, I decided to post my response here. Below is a link to the article referenced: https://hbr.org/2019/07/building-a-startup-that-will-last
The article is interesting, but emphasizing “second and third acts” assumes that the start-up will successfully navigate the first act. Even with addressing what the author views as key points this is still a very big assumption. The reasons for Longevity and Success are far more complex and multi-dimensional, but it highlights some of the more important areas of focus.
Long-term success requires several things: The right combination of having a unique goal that has the potential to make a big impact (think “No software” from Salesforce.com); Innovative ideas to achieve that goal; A diverse team to build the product (a mix of visionaries, insightful “translators,” technical experts, designers, planners, adept doers, etc.); Very good sales / business development / marketing to describe a better way of doing things and converting that to new business; and ultimately a management team focused on sustainable and scalable growth.
The point about the need to “Articulate a value framework oriented toward societal impact, not just financial achievement” seems superficial and too tactical.
First, there are unintended consequences to most new technologies. Social Media is a recent example, but Genetic Editing and AI are two areas that are likely to provide more examples over the next decade. Not every societal impact will be positive, and having a negative impact could very well lead to the untimely demise of that company.
Second, the two ideas (societal impact and financial achievement) are not mutually exclusive. When I owned my consulting company, we aimed to fund $1M of medical research to find a cure for Arthritis. We allocated half of our net profits to this goal. Every employee was on board with this because there was a tangible example of why it mattered (my daughter). We invested $500K and helped launch a few careers for some brilliant MD/Ph. Ds and at least one national protocol came out of their research.
Mission and Vision are important to a company, yet many fail to view this as anything more than a marketing effort. Those companies fail to realize that this is as much to motivate and inspire their employees as it is to grab a prospective customer’s attention. These should be inspirational and aspirational, such as the “BHAG” (Big Hairy Audacious Goals) Collins and Porras wrote about 25 years ago.

Regarding Endurance and the assertion that “…the best businesses are intrinsically aligned with the long-term interests of society,” my take is slightly different. The best businesses are always looking for trends and opportunities in an ever-changing global competitive landscape instead of looking to their competitors and trying to ride on their coattails. Companies with a culture of fostering innovation as a way to learn and grow (Amazon and Google are two great examples) are able to find that intersection of “good business” and “positive societal impact.” It is much more complex than a simple one-dimensional outlook.
But it was a good article to help reframe ideas and assumptions around growth.
One Successful Approach to Innovation that worked for an SMB
When I owned a consulting company, we viewed innovation as an imperative. It was the main thing that created differentiation, credibility, and opportunity. We had an innovation budget, solicited ideas from the team, and evaluated those ideas quarterly.
Almost as important to me was that this was fun. It allowed everyone on the team to suggest ideas and participate in the process. That was meaningful and supported the collaborative, high-performance culture that had developed. The team was inspired and empowered to make a difference, and that led to an ever-increasing sense of ownership for each employee.
The team also had a vested interest in having the process work, as quarterly bonuses were paid based on their contributions to the company’s profitability. There was a direct cause-and-effect correlation with tangible benefits for every member of the team.
We developed the following 10 questions to qualify & quantify the potential of new ideas:
- What will this new thing do?
- It is important to be very detailed as this was used to create a common vision of success based on the presented idea.
- What problem(s) does this solve, and how so?
- This seems obvious, but selling this new product will be an uphill challenge if you are not solving a problem (which could be something like “lack of organic expansion”) or addressing a pain point.
- What type of organizations have those problems and why?
- This was fundamental to understanding if a fix was possible from a practical perspective, what the value of that fix might be for the target buyer, and how much market potential existed to scale this new offering.
- What other companies have created solutions or are working on solutions to this problem?
- The lack of competition today does not mean you are the first to attack this problem. Due diligence can help avoid repeating the failure of others, potentially providing lessons learned by others and helping you avoid similar pitfalls.
- Will this expand our existing business, or does it have the potential to open up a new market for us?
- Each answer has upsides and downsides, but breaking into a new market can take more time and be more difficult, time-consuming, and expensive to achieve.
- Is this Strategic, Tactical, or Opportunistic?

- An idea may fall into multiple categories. When the Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) Act became law, we viewed a new service offering as a tactical means to protect our managed services business and an opportunistic means to acquire new customers and grow the business. While this is not true innovation, IMO, it was an offering that flowed from this defined process.
- What are the Cost, Time, and Skill estimates for developing a Minimally Viable Product (MVP) or Service?
- What are the Financial Projections for the first year?
- Cost to develop and go to market.
- Target selling price, factoring in early adopter discounts.
- Estimated Contribution Margin Ratio (for comparison with other ideas being considered).
- Break-even point.
- Would we be able to get an existing customer to pre-purchase this?
- A company willing to provide a PO that commits to purchasing that MVP within a specific timeframe increased our confidence in the viability of the idea.
- What are the specific Critical Success Factors to be used for evaluation purposes?
- This important lesson learned over time helped minimize emotional attachment to the idea or project and provided objective milestones for critical go / no-go decision-making.
This process was purposeful, agile, lean, and somewhat aggressive. We believed it gave our company a competitive advantage over larger companies that tended to respond slower to new opportunities and smaller competitors that did not want to venture outside their wheelhouse.
With each project, we learned and became more efficient and effective and made better investment decisions that positively impacted our success. We monitored progress on an ongoing basis relative to our defined success criteria and adjusted or sunset an offering if it stopped providing the required value.
The process was not perfect…
For example, we passed on some leading-edge ideas, such as a “Support Robot” in 2003, an interactive program that used a machine-learning algorithm. It was to be trained using historical log files, could quickly and safely be tested in a production environment, refined as needed, and ultimately validated.
This automation could have been used with our existing managed services and Remote DBA customers to further mitigate the risk of unplanned outages. Most importantly, it would have provided leverage to take on new business without jeopardizing quality or adding staff – thereby increasing revenue and profit margin.
At the time, we believed this would be too difficult to sell to prospective customers (“pipe dream” and “snake oil” were some of the adjectives we envisioned), so it appeared to lack a few items required by the process. Live and learn.
In summary, having a defined approach for something as important as business needs innovation to grow and prosper, as best demonstrated by market leaders like Amazon and Google (read the 10-K Annual Reports to gain a better understanding of their competitive growth strategies that are largely based on innovation).
Implementing this type of approach within a larger organization requires additional steps, such as getting the buy-in from a variety of stakeholders and aligning with existing product roadmaps, but it is still the key to scalable growth for most businesses.